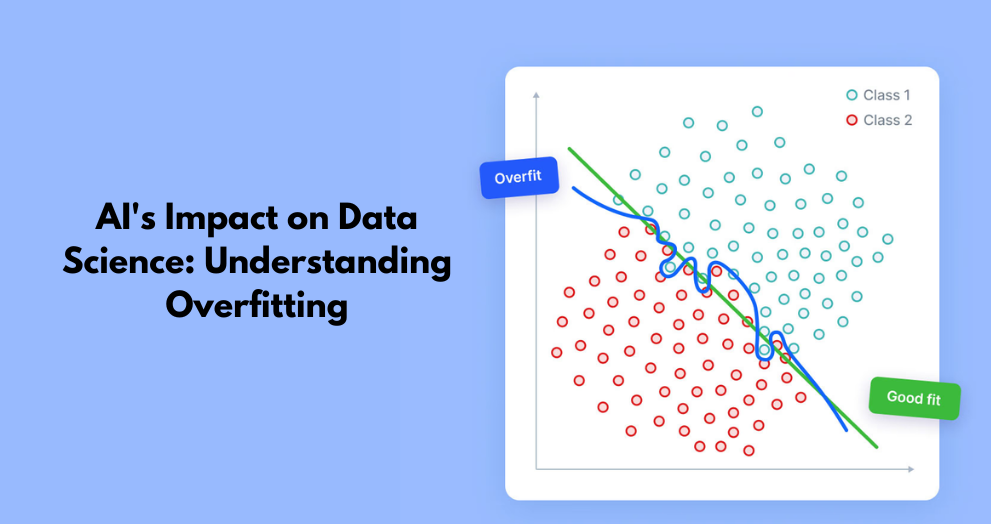
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly influenced data science practices, enabling businesses and researchers to analyze vast amounts of data and derive meaningful insights. AI-driven models help make better predictions, automate decision-making processes, and enhance productivity across industries. However, one of the major challenges in AI and machine learning is overfitting. This phenomenon can hinder a model’s performance, leading to unreliable predictions. In this article, we will explore overfitting in-depth, understand its causes, implications, and solutions, and discuss how AI continues to shape data science practices.
What is Overfitting?
Overfitting occurs when a machine learning model learns the training data too well, including both meaningful patterns and random noise. As a result, the model performs exceptionally well on the training dataset but fails to generalize to new, unseen data. In simple terms, an overfitted model memorizes rather than learns, making it ineffective for real-world applications.
Real-World Analogy
Imagine a student preparing for an exam. Instead of understanding concepts, they memorize the exact answers to previous test questions. When they face a new set of questions in the actual exam, they struggle because they didn’t develop a deep understanding of the subject. Similarly, an overfitted AI model can’t adapt to new scenarios, reducing its effectiveness in real-world applications.
Why Does Overfitting Happen?
Several factors contribute to overfitting in AI and machine learning models:
1. Excessive Complexity in Training Data
If a dataset contains a high level of noise or unnecessary details, the model may pick up on irrelevant patterns. Instead of focusing on core insights, it memorizes noise, leading to poor generalization.
2. Small Training Dataset
When a model is trained on limited data, it lacks the exposure needed to generalize patterns. As a result, it learns the training data too precisely, making it ineffective when new data is introduced.
3. Too Many Features
If a dataset contains too many features, the model may struggle to identify which ones are truly important. This leads to excessive reliance on specific attributes, increasing the likelihood of overfitting.
4. Lack of Proper Validation
Without testing the model on separate validation datasets, there is no way to ensure its ability to generalize. Cross-validation techniques help detect overfitting before deploying models in real-world applications.
Impact of Overfitting on Data Science
Overfitting can have severe consequences, especially in industries where AI-powered decisions are critical. Here are some examples:
1. Healthcare
In medical diagnosis, overfitted models may show high accuracy during training but fail when applied to new patient data. This can lead to incorrect diagnoses and ineffective treatment recommendations.
2. Finance
Overfitting in financial models can result in misleading predictions about stock trends, leading to poor investment decisions.
3. Marketing and Customer Insights
Businesses use AI to analyze customer behavior and predict future trends. An overfitted model may make assumptions based on limited data, leading to ineffective marketing strategies.
How to Prevent Overfitting?
To develop AI models that perform well in real-world applications, data scientists employ several techniques to reduce overfitting:
1. Increase the Size of Training Data
A larger dataset exposes the model to more scenarios, helping it learn generalized patterns instead of memorizing specifics.
2. Feature Selection
By selecting only the most relevant features, data scientists can reduce complexity and prevent the model from relying on irrelevant details.
3. Regularization Techniques
Methods like L1 and L2 regularization penalize excessive reliance on specific parameters, forcing the model to learn more general patterns.
4. Cross-Validation
Using k-fold cross-validation ensures that the model performs consistently across different subsets of data.
5. Dropout in Neural Networks
In deep learning, dropout is a technique where random neurons are deactivated during training to prevent excessive reliance on specific nodes.
The Role of AI in Enhancing Data Science
Artificial Intelligence continues to evolve, enhancing the way data science operates across industries. AI-powered tools allow data scientists to:
-
Automate data preprocessing and cleaning
-
Identify meaningful patterns in large datasets
-
Make more accurate predictions through advanced algorithms
-
Optimize decision-making in businesses
However, with these advancements, addressing overfitting is crucial and ensuring AI models remain reliable and adaptable. Many professionals looking to enter the field of AI and machine learning seek the Best Data Science Training in Delhi, Noida, Lucknow, Meerut, Indore, and more cities in India to develop the necessary skills for handling these challenges effectively. High-quality training programs provide hands-on experience with machine learning algorithms, model evaluation techniques, and real-world applications, helping learners become proficient in AI-driven data science practices.
Conclusion
Overfitting is a fundamental challenge in AI-driven data science. Understanding how it affects model performance and learning effective prevention techniques is crucial for building reliable AI systems. As AI continues to shape data science practices, ensuring models generalize well remains a top priority for professionals in the field. Investing in quality training and staying updated with AI advancements will help data scientists develop impactful and scalable solutions.