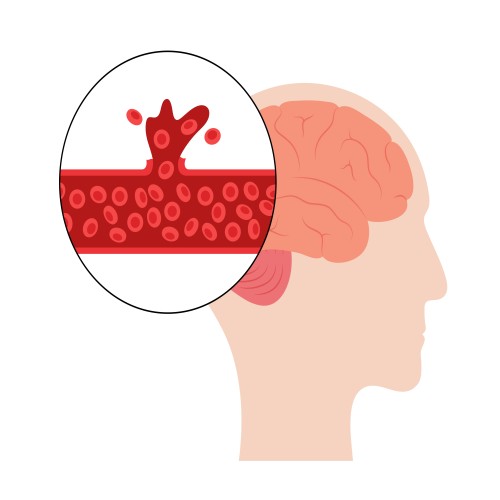
A brain blood clot is a serious medical condition that can lead to strokes and other complications. When a clot forms inside blood vessels in the brain, it can prevent oxygen-rich blood from reaching the area, thus causing damage to that area. It is very vital to understand the different types of brain blood clots and their management for early detection and proper management.
Types of Brain Blood Clots
1. Thrombotic Clot (Cerebral Thrombosis)
A thrombotic clot forms in an artery supplying blood to the brain. It develops due to the buildup of plaque (fat and cholesterol) in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. When plaque narrows the arteries, blood flow slows, creating an ideal milieu for clotting.
Cause:
-
Cholesterol
-
Blood pressure
-
Lifestyle
-
Diabetes
-
Physical inactivity
Symptoms:
-
Sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body
-
Difficulty speaking
-
Difficulty walking
-
Problems with vision
-
Intense headache
2. Embolic Clot (Cerebral Embolism)
With embolism, the clot is formed at a distant site, usually in the heart, and travels to obviate an artery in the brain from supplying blood to certain regions of the brain. This phenomenon commonly occurs with heart problems such as atrial fibrillation.
Cause:
-
Atrial fibrillation
-
Heart valve diseases
-
Infections of the heart
-
Blood clotting disorders
Symptoms:
-
Sudden weakness, paralysis of the face, arm, or leg
-
Difficulty in speaking or understanding speech
-
Loss of coordination
-
Severe dizziness
3. Venous Clot (Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis – CVST)
CVST occurs when a clot forms in the veins that drain blood from the brain. This hinders the exit of blood from the brain, causing its buildup; the consequence is an elevation in intracranial pressure and the possibility of bleeding into the brain.
Cause:
-
Pregnancy and childbirth
-
Use of contraceptive pills
-
Dehydration
-
Blood clotting disorders
-
Head trauma
Symptoms:
-
Severe headache
-
Seizures
-
Vision problems
-
Confusion
-
Nausea and vomiting
4. Hemorrhagic Clot (Bleeding Clots in the Brain)
A hemorrhagic clot forms when there is a rupture in the blood vessels in the brain. There are several causes of bleeding inside the skull, among them: high blood pressure, trauma, or aneurysms, thin-walled blood vessels that bulge and rupture.
Cause:
-
Uncontrolled hypertension
-
Head injury
-
Aneurysmal rupture
-
Anticoagulants
Symptoms:
-
Sudden severe headache
-
Loss of consciousness
-
Feeling weak or numb
-
Speech problems or swallowing difficulty
-
Nausea and vomiting
How Brain Blood Clots Are Treated
1. Medications
Medications are the most important component of the management of brain blood clots in the acute phase.
Blood Thinners (Anticoagulants)
They prevent new clots from forming or stop the already present clots from growing:
Heparin and warfarin
Standardly used for the management of embolic and venous clots.
Clot-Busting Drugs (Thrombolytics)
-
Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is a drug that dissolves clots fast, restoring blood flow.
-
Used for the treatment of ischemic strokes caused by thrombotic or embolic clots.
-
Must be delivered within a few hours after the onset of stroke symptoms.
2. Surgical Treatments
Surgery may need to be undertaken in cases where medication fails to dissolve or break up clots.
Thrombectomy
-
In this procedure, the doctors remove the clot from the artery with a catheter.
-
This is effective in cases of large thrombotic or embolic clots causing stroke.
Stenting
-
A small mesh tube (stent) is inserted into a narrowed artery to prevent its from closing.
-
improving blood flow.
Craniotomy
-
This is surgery to remove a portion of the skull to relieve pressure caused by hemorrhagic clots.
-
It is used in severe head bleeding cases.
3. Lifestyle Changes to Prevent and Manage
Preventing blood clotting in the brain is the best measure. Therefore, healthy habits minimize the chances of forming clots and improve recovery.
Nutritious Diet
-
Eat foods high in fiber, fruits, and vegetables.
-
Reduce salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
Regular Exercise
-
Keeps the heart healthy and improves blood circulation.
-
Exercise for about half an hour on most days in a week.
Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol
-
Smoking destroys vessels and causes clot formation.
-
Excessive intake of alcohol raises blood pressure.
Control Health Conditions
-
Management of high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes through medication as well as lifestyle changes.
-
Annual checkup for doctors to monitor heart health.
4. Treatment of Emergency Stroke
Emergency care is essential when a blood clot in the brain leads to a stroke.
The FAST Stroke Recognition Method:
-
Face: One side of the face droops.
-
Arms: One arm drifts downwards when raised.
-
Speech: Speech is slurred or strange.
-
Time: Call emergency services immediately if you notice these signs.
Conclusion
At DrPro, blood clots inside the brain are very dangerous and can lead one into serious health problems if treatment is not timely. If one understands all the different kinds of clots like thrombotic, embolic, venous, and hemorrhagic, one can catch symptoms early. These treatments include medicines, surgeries, and lifestyle changes to prevent further clots. Anyone with such symptoms of brain blood clotting should immediately seek medical help. Lives can be saved with minor intervention for effective recovery.